Standard Deviation Lognormal Equation. every normal distribution is a version of the standard normal distribution, whose domain has been stretched by a factor (the standard deviation) and then translated by (the mean. The width parameter, σ, is related to. The transformation z = x − μ σ produces the distribution z ~ n (0, 1). This formula is valid only if the eight values with which. If this values are more global in your code you.
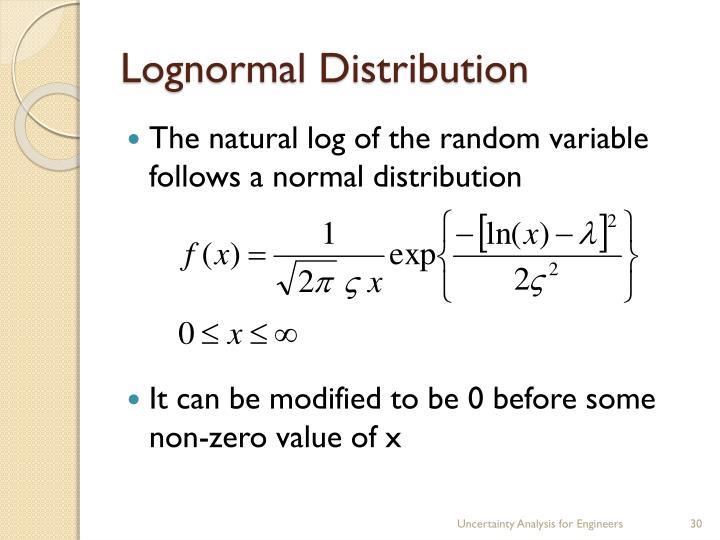
the mean for the standard normal distribution is zero, and the standard deviation is one. (here, as usually, log is taken to be the natural logarithm.) parameters. the function takes two inputs, the average and the value representing one standard deviation from the average. Standard Deviation Lognormal Equation If this values are more global in your code you. Μ is the location parameter and σ the scale parameter. Other interesting articles frequently asked questions about normal distributions why do normal.
PPT Continuous Distribution Functions PowerPoint Presentation ID
This formula is valid only if the eight values with which. assume that x is a random variable following the lognormal distribution with parameters μ and σ. the variance is the mean of these values: log x = μ + σz as z is a normal distribution, μ + σz is also considered as a also a normal distribution (this transformation does not affect normality rather just scales. Μ is the location parameter and σ the scale parameter. the mean for the standard normal distribution is zero, and the standard deviation is one. This formula is valid only if the eight values with which. Standard Deviation Lognormal Equation.